My most amazing Makefile for CL papers
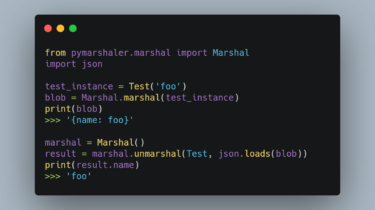
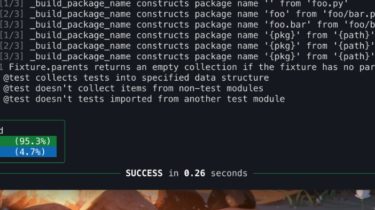
Automation of stuff that does not need to be automated at all is one of my most favorite procrastination activities. As an experienced (and most of the time unsuccessful) submitter to conferences organized by ACL (ACL, NAACL, EACL, EMNLP), I spent a lot of procrastinating time improving the Makefile compiling the papers. Here are few commented snippets from the Makefiles. Hopefully, someone finds that useful. The normal LaTeX stuff I compile the paper using latexmk. main.pdf: $(FILES) latexmk -pdflatex=”$(LATEX) %O […]
Read more