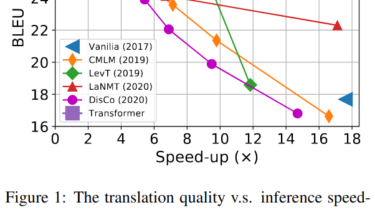
Hugging Face – Special Edition – New Plans, Private Models and AutoNLP – Dec 23rd 2020
News Ho Ho Ho! welcome to a special edition of the Hugging Face newsletter focused on new and upcoming commercial products. 👩🔬Introducing Supporter plans for individuals, with private models 👩🔬 Hugging Face is built for, and by the NLP community. We share our commitment to democratize NLP with hundreds of open source contributors, and model contributors all around
Read more