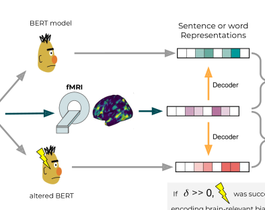
Does injecting linguistic structure into language models lead to better alignment with brain recordings?
Figure 1 shows a high-level outline of our experimental design, which aims to establish whether injecting structure derived from a variety of syntacto-semantic formalisms into neural language model representations can lead to better correspondence with human brain activation data. We utilize fMRI recordings of human subjects reading a set of texts. Representations of these texts are then derived from the activations of the language models. Following Gauthier and Levy (
Read more