A client to digitalize the boring parts of monopoly with python
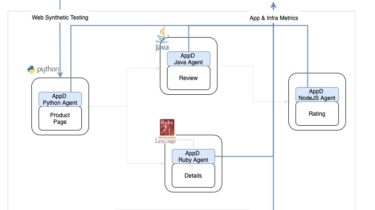
Pinopoly A client to digitalize the boring parts of monopoly What is this? Pinopoly is a tool to remove the “banker” player and replace them with a digitalized system. It is intended to be used on a Raspberry Pi but can be used in the command line as well. How to use Running python3 -m monopoly will open the user interface Useful GitHub https://github.com/alexover1/pinopoly
Read more