An ActivityWatch watcher to pose questions to the user and record her answers
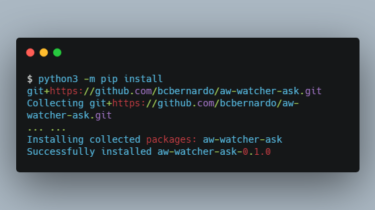
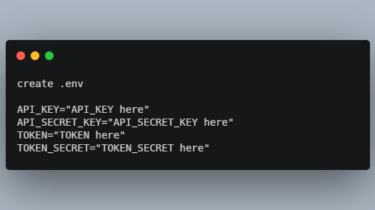
aw-watcher-ask An ActivityWatch watcher to pose questions to the user and record her answers. This watcher uses Zenity to present dialog boxes to the user, and stores her answers in a locally running instance of ActivityWatch. This can be useful to poll all sorts of information on a periodical or random basis. The inspiration comes from the experience sampling method (ESM) used in psychological studies, as well as from the quantified self movement. Install Using pip/pipx Create a virtual environment, […]
Read more