Text Analysis & Topic Modelling with spaCy & GENSIM
Apply Topic Modeling algorithms using Gensim — before moving on to more advanced textual analysis techniques
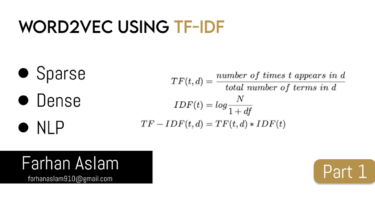
Read moreWord toVector for Natural Langauge Processing, Word2Vec using tf-idf
Hi Folks, If you are a data scientist working with machine learning models you may know that our model understands numerical values. While working with Natural language processing to make our models understand our words we need to embed our words into vectors.
Read moreMinun and Explainable Entity Matching
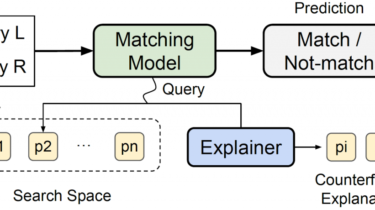
Given two collections of entities, such as product listings, the entity matching (EM) problem aims to identify all pairs that refer to the same object in the real world, such as products, publications, businesses, etc. Recently, deep learning (DL) techniques have been widely applied to the EM problem and have achieved promising results. Unfortunately, the performance gain brought by DL techniques comes at the cost of reducing transparency and interpretability. The reason is that DL-based approaches are more like black-box […]
Read moreUsing Conda? You might not need Docker
Docker packaging is useful, but doing it well is not easy. Even limiting the scope of discussion to production use of Python applications, the number of details to cover is extensive enough that I’ve written over 50 articles on the topic, and created a number of products to speed up the packaging process. In a better universe, none of this would be necessary. So while Docker is often useful enough to merit this effort, in some situations you might be […]
Read moreImplementing Simple Text Summarizer in Python using spaCy
A step-by-step guide to summarizing text using NLP
Read moreUpcycle High Cardinality Features Using Topic Modeling
Photo by Cybèle and
Read moreLearn any Algorithm and its implementation in any Programming Language
Image from Figma designer (
Read moreAnálise Exploratória de Dados: House Prices — Advanced Regression Techniques
Neste artigo, será realizada uma análise exploratória de dados referente a um dataset intitulado: House Prices — Advanced Regression Techniques obtido no kaggle. O link para o repositório no github contendo o código utilizado nessa análise será disponibilizado ao final do artigo.
Read more