Implementation of different architectures for emotion recognition in conversations
Emotion Recognition in Conversations
Unlike other emotion detection models, these techniques consider the party-states and inter-party dependencies for modeling conversational context relevant to emotion recognition. The primary purpose of all these techniques are to pretrain an emotion detection model for empathetic dialogue generation.
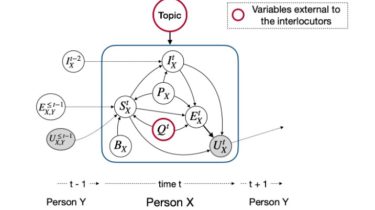
Interaction among different controlling variables during a dyadic conversation between persons X and Y. Grey and white circles represent hidden and observed variables, respectively. P represents personality, U represents utterance, S represents interlocutor state, I represents interlocutor intent, B represents background knowledge, Q represents external and sensory inputs, E represents emotion and Topic represents topic of the conversation. This can easily be extended to multi-party conversations.
Emotion recognition can be very useful for empathetic and affective dialogue generation –
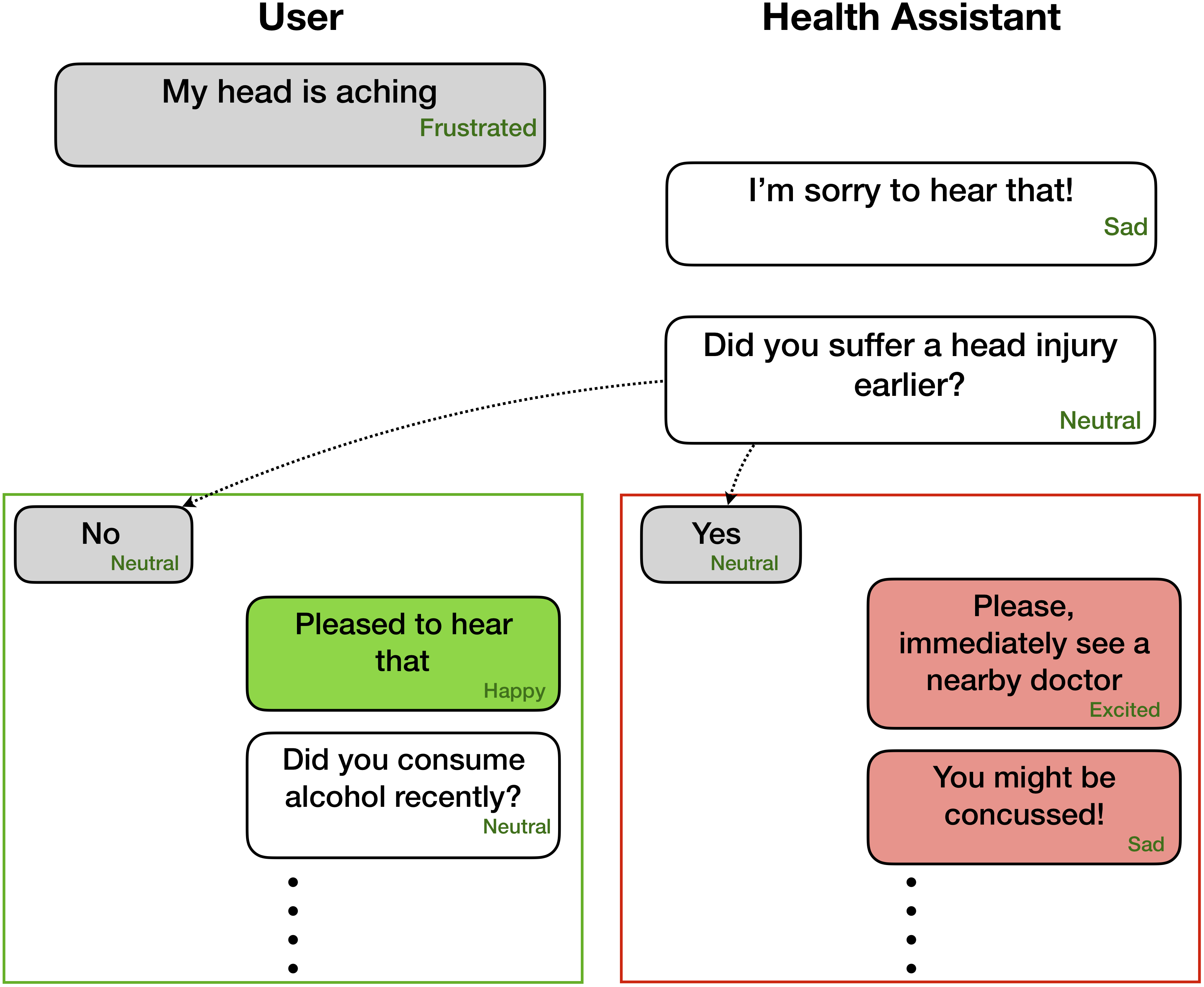
Data Format
These networks