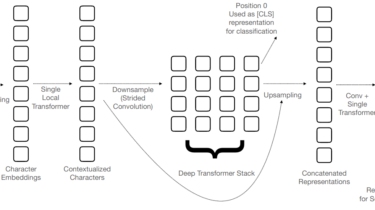
Machine Translation Weekly 76: Zero-shot MT with pre-trained encoder
Using pre-trained multilingual representation as a universal encoder for machine translation might seem like an obvious thing to try: train a decoder into one target language using one or several source languages and you get a translation from 100 languages into the target language. This sounds great, but this is not how it works. (Or it works somehow, but not really well, I tried it myself.) Recently, I came across a pre-print where the authors figured out how to do […]
Read more