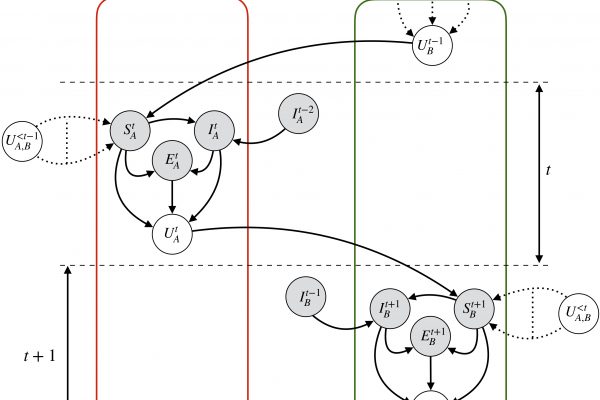
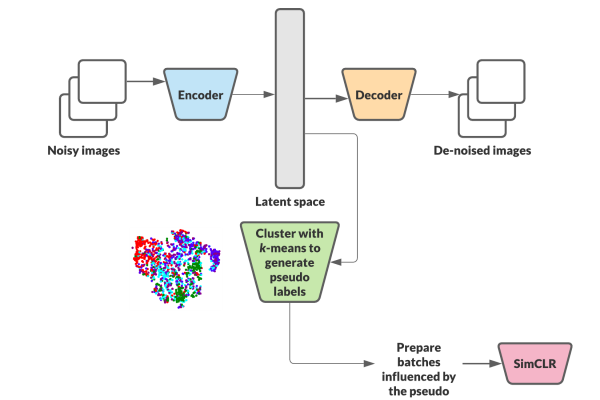
G-SimCLR: Self-Supervised Contrastive Learning with Guided Projection via Pseudo Labelling
In the realms of computer vision, it is evident that deep neural networks perform better in a supervised setting with a large amount of labeled data. The representations learned with supervision are not only of high quality but also helps the model in enhancing its accuracy… However, the collection and annotation of a large dataset are costly and time-consuming. To avoid the same, there has been a lot of research going on in the field of unsupervised visual representation learning […]
Read more