A Gentle Introduction to Statistical Tolerance Intervals in Machine Learning
Last Updated on August 8, 2019
It can be useful to have an upper and lower limit on data.
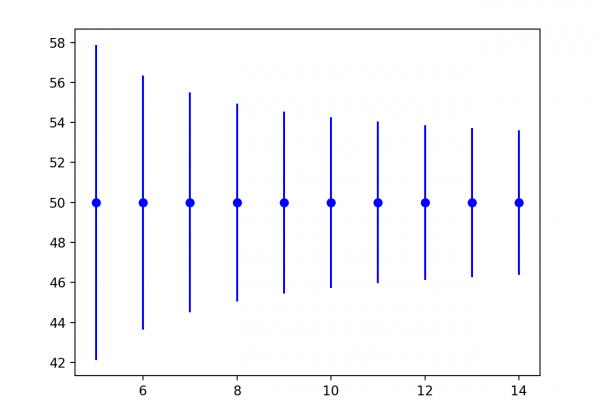
These bounds can be used to help identify anomalies and set expectations for what to expect. A bound on observations from a population is called a tolerance interval. A tolerance interval comes from the field of estimation statistics.
A tolerance interval is different from a prediction interval that quantifies the uncertainty for a single predicted value. It is also different from a confidence interval that quantifies the uncertainty of a population parameter such as a mean. Instead, a tolerance interval covers a proportion of the population distribution.
In this tutorial, you will discover statistical tolerance intervals and how to calculate a tolerance interval for Gaussian data.
After completing this tutorial, you will know:
- That statistical tolerance intervals provide a bounds on observations from a population.
- That a tolerance interval requires that both a coverage proportion and confidence be specified.
- That the tolerance interval for a data sample with a Gaussian distribution can be easily calculated.
Kick-start your project with my new book Statistics for Machine Learning, including step-by-step tutorials and the Python source code files for all
To finish reading, please visit source site